Thermal insulation of pipelines: ways to solve the problem
It is possible to provide effective protection for piping systems from environmental factors, mainly from the outside temperature, if the following measures are taken:
- creation of a heating system using heating cables. This method involves performing work on fixing heating elements on top of household pipelines or setting up a device inside the collector. Heating elements work from the electrical network. Please note that when continuous heating of pipelines is performed, then self-regulating wires are used, which are switched on and off automatically. The use of such heating systems excludes situations of overheating of structures;
- laying of pipelines below the level of soil freezing. This option of their placement eliminates the contact of networks with sources of cold;
- the use of closed underground boats. The air space is isolated, so the air around the pipes cools slowly. And this allows you to exclude freezing of the coolant or other contents of the pipes;
- creation of a circuit of heat-insulating materials to ensure high thermal protection of pipelines. This is the most common type of pipeline protection.
Since the latter method is most often used, it makes sense to talk about it in more detail.
Power plants
All objects with a coolant temperature above 45 ° C, located indoors, and with a temperature above 60 ° C, located outdoors, are subject to thermal insulation. In addition, pipelines and cold water tanks located indoors should be insulated to prevent condensation of moisture from the ambient air on their surface, and when located outdoors, they should be insulated in order to exclude the possibility of freezing in case of emergency (short-term) interruptions of movement. water. The design of thermal insulation at power plants should be based on the "Standards for the design of thermal insulation" [L. 81, "Rules for the technical operation of power plants and networks" - §§ 190 and 332, "Building codes and regulations" [L. 101, "Typical details of thermal insulation of pipelines and equipment" 1L. 12], as well as special departmental requirements and instructions, if any. Typical parts of the TS-02-11 series, approved by the USSR Gosmontazh-specialstroy, were put into effect on August 1, 1964 to replace the TS-02-01 series of 1957. They consist of four albums illustrating: 1) products for thermal insulation of pipelines and equipment; 2) thermal insulation of pipelines with a positive temperature; 3) thermal insulation of fittings and flange connections of pipelines with a positive temperature; 4) thermal insulation of industrial equipment with a positive temperature. It should be borne in mind that in the tables of the scope of work in the "Typical parts" of the TS-02-11 series, inaccuracies are allowed, therefore it is recommended to use only structural drawings of "Typical parts" in projects. The project should provide for the most effective heat-insulating materials, and heat-insulating structures should be prefabricated, ensuring the production of heat-insulating works by high-speed and industrial methods. When designing thermal insulation, different requirements for thermal insulation materials and structures must be taken into account.The correct choice of heat-insulating materials and high-quality performance of heat-insulating works ensure the durability of heat-insulating structures. The applied heat-insulating materials and structures should be non-scarce, relatively cheap, transportable, not combustible. They must retain their heat-shielding and physical properties during the entire service life, not prevent thermal deformations of pipelines and equipment during heating and cooling (if necessary, provide expansion joints), withstand object vibrations and not cause corrosion of metal walls. to buy a profile pipe 80x80x3 at low prices The choice of heat-insulating structures should be made taking into account the conditions for the location of equipment and routing of pipelines, as well as based on the requirements for installation and operation of thermal insulation. For items of equipment and pipelines (fittings, flange connections, etc.) that require systematic monitoring during operation, collapsible heat-insulating structures should be used. Heat-insulating structures of corners and bends of pipelines and expansion joints should not impede the temperature movements of objects and should not be subject to cracking and destruction, which is ensured by the use of elastic heat-insulating materials and the device of expansion joints. The blind part of the body of various shaped parts can be covered with a non-separable insulating structure. When insulating vertical sections of pipelines or vertical equipment, support shelves should be arranged to transfer the load from the weight of the thermal insulation structure along the sections to the insulation object.
Standards for thermal insulation of pipelines
Requirements for thermal insulation of equipment pipelines are formulated in SNiP. The regulatory documents contain detailed information about the materials,
which can be used for thermal insulation of pipelines, and besides this methods of work. In addition, in the regulatory documents
standards for thermal insulation contours are indicated, which are often used to insulate pipelines.
The SNiP contains the following recommendations for thermal insulation of pipelines:
- regardless of what temperature the coolant has, any pipeline system must be insulated;
- both ready-made and prefabricated structures can be used to create a heat-insulating layer;
- corrosion protection must be provided for the metal parts of the pipelines.
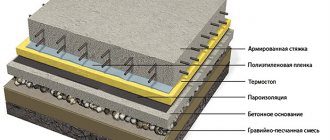
It is desirable to use a multilayer loop structure for pipe insulation. It must include the following layers:
- insulation;
- vapor barrier;
- protection made of dense polymer, non-woven fabric or metal.
In some cases reinforcement can be built, which eliminates the crushing of materials, and in addition, prevents deformation of the pipes.
It should be noted that most of the requirements contained in regulatory documents relate to the isolation of high-capacity main pipelines. But even in the case of installing household systems, it will be useful to get acquainted with them and take them into account when installing water supply systems for sewerage on our own.
Polyurethane foam insulation for heating systems
Pipes in polyurethane foam - areas of use and technical characteristics:
GOST 30732-2006 regulates technical conditions for pipes with polyurethane foam insulation and stipulates their scope in the following conditions: Pipes in a PE sheath are designed for underground laying of heating networks by the channelless (lowering into earthen trenches) method. Pipes in a protective metal sheath are designed to be laid in openings, tunnels and on the ground. The operating pressure in the system must not exceed 1.6 bar.Carrier temperature - up to + 140 ° C, or + 150 ° C when operating in highways with its values in the range from + 70 ° to + 150 ° C. It is allowed to use pipeline highways for water supply and sewerage, oil and gas supply, in engineering networks of production when moving liquids from tanks, large containers and storages.
Advantages of PU foam insulation
Insulation from polyurethane foam on pipes and their use has the following advantages over other technologies:
In everyday life, foam rubber from polyurethane foam is widely used as a heater, the foam material is its solid analogue, belongs to the class of foam plastics - materials that have air cells in their structure. High-quality factory production of products allows pipelines to be lowered directly into the ground, under water without additional devices. Among analogues - polyvinyl chloride, phenol-formaldehyde, urea-formaldehyde and polystyrene polyurethane foams, polyurethane has the lowest thermal conductivity (0.02 W / m * K) - almost two times less than that of foam. When installing a pipeline with ready-made thermal insulation, the speed of work increases significantly, enterprises manufacture finished shaped products in thermal insulation (tees, bends, transitions, branches) to simplify installation. The heat-insulating layer, applied in the factory, is hermetically sealed and of high quality; one of its important additional properties is to provide reliable protection against corrosion. The presence of built-in copper indicator conductors allows detecting areas of thermal insulation with high humidity - this simplifies repair and restoration work in the event of a line break. PPU pipelines are designed for long-term operation without maintenance for a minimum period of 30 years. To increase it, the galvanized shell is often coated with special protective compounds (varnishes, paints, polymers), which perform anti-corrosion functions during operation and can be repeatedly renewed.
Materials for thermal insulation of pipelines
At the moment, the market offers a large selection of materials that can be used to insulate pipelines. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages, as well as application features. To choose the right heat insulator, you need to know all this.
Polymer heaters
When the task is to create an effective system for thermal insulation of pipelines, most often attention is paid to foamed polymers. A large assortment allows you to choose the right material, thanks to which you can provide effective protection from the external environment and eliminate heat loss.
If we talk in more detail about polymeric materials, then the following can be distinguished from those available on the market.
Polyethylene foam.
The main characteristic of the material is its low density. Moreover, it is porous and has a high mechanical strength. This insulation is used to make cut cylinders. Their installation can be performed even by people far from the sphere of thermal insulation of pipelines. However, this material has one drawback: structures made of polyethylene foam, have fast wear and in addition to this, they have poor thermal stability.
If polyethylene foam cylinders are chosen for thermal insulation of pipelines, then special attention should be paid to their diameter. It must match the collector diameter. Considering this rule when choosing a design of insulation, it is possible to exclude spontaneous removal of casings made of polyethylene foam.
Expanded polystyrene.
The main feature of this material is elasticity. It is also characterized by high strength indicators.Protective products for thermal insulation of pipelines from this material are produced in the form of segments, which in their appearance resembles a shell. Special locks are used to connect parts. They have spikes and grooves, thanks to which the quick installation of these products is ensured. The use of a polystyrene foam shell with technical locks excludes the occurrence of "cold bridges" after installation. In addition, there is no need for additional fasteners during installation.
Polyurethane foam.
This material is used mainly for pre-installed thermal insulation of heating network pipelines. However, it can also be used to insulate household piping systems. This the material is produced in the form of foam or shell, which consists of two or four segments. Spray insulation provides reliable thermal insulation with a high degree of tightness. The use of such insulation is most suitable for communication systems with complex configurations.
Using polyurethane foam in the form of foam for thermal insulation of pipelines of heating networks, you need to know that it is destroyed under the influence of ultraviolet rays. Therefore, in order for the insulating layer to serve for a long time, it is necessary to ensure its protection. For this, a layer of paint is applied over the foam or a non-woven fabric with good permeability is laid.
Fibrous materials
Heaters of this type are mainly represented by mineral wool and its varieties. At present they are the most popular among consumers as a heater. Materials of this type are in good demand as well as polymeric materials.
Thermal insulation made with fiber insulation has certain advantages. These include the following:
- insignificant coefficient of thermal conductivity;
- the resistance of the heat-insulating material to the effects of aggressive substances such as acids, alkalis, oil;
- the material is able to maintain a given shape without an additional frame;
- the cost of the insulation is quite acceptable and affordable for most consumers.
Please note that during work on thermal insulation of pipelines with such materials shrinkage of the fiber must be avoided when laying insulation. It is also important to protect the material from moisture.
Products made of polymer and mineral wool insulation for thermal insulation in some cases can be covered with aluminum or steel foil. The use of such screens will reduce heat dissipation.
Protection of the heat-insulating layer of external heating mains
Outdoor heating networks, or, as they are also called, air or overhead, are laid in cases of need for temporary construction of a heating main (bybas) or in those places where it is impossible to lay a heating network underground. For example, in earthquake-prone areas. Such heating networks are convenient in operation, are quickly built and differ from other types of heating networks by their low cost.
Thermal insulation of external pipelines. Thermal insulation materials.
They are used as materials for insulation of external heating mains. 1. Thermal insulation of pipes with mineral wool.
Advantages: - mineral wool is practically not hygroscopic - with properly organized ventilation, if it gets wet, it immediately gives off excess moisture; - ensures the stability of its physical and chemical properties throughout the entire period of operation; - has a sufficiently long service life. Disadvantages: - when wet, it loses its performance properties; - has weak strength and is inferior in this characteristic to other heat-insulating materials.



2. Thermal insulation of pipes by PPU dusting, use of PPU-shells. Advantages: - the ability to create continuous insulation, without joints; - is a sufficiently elastic material; - provides the possibility of quick installation; - is a biologically neutral material, not subject to decay, resistant to microorganisms and mold; - provides stable thermal insulation properties in a wide temperature range. Disadvantages: - is a fairly flammable material and, when burned, emits highly toxic substances into the surrounding space; - spraying requires special equipment; - does not "breathe". In recent years, the method of thermal insulation of pipes with PU foam shells has become widespread, but they also need additional protection.
3. Thermal insulation of pipes with foam concrete.
Advantages: - high thermal insulation qualities, not inferior to polyurethane foam insulation; - solidity, due to which good anti-corrosion protection is provided due to the absence of cold bridges and the impossibility of plundering material; - high manufacturability, which makes it possible to lay heating mains in any area; - high adhesive properties. Disadvantages: - restrictions on the thickness of the insulation; - the need to protect the dried surface with a protective layer. 4. Reinforced concrete (reinforced concrete).
Advantages: - effective thermal insulation is provided; - there is no possibility of theft. Disadvantages: - high cost; - the complexity of the installation work; - rather high brittleness of the material.


It's obvious that each type of thermal insulation layer must be protected. If this is not done, then over time, under the influence of unfavorable external factors, it will be disrupted. Practice shows that non-insulated heat-shielding layers quickly fall apart, crumble, rot, and it is necessary to carry out work on their replacement. That is why, today, external protective pipe insulation is actively used.
Waterproofing of the heat-insulating layer. Review of basic materials.
We have to admit that almost all types of such insulation have great disadvantages:
– fiberglassb - extremely short-lived, after 1 year, the heating main, insulated with fiberglass, is literally unrecognizable. The fabric turns into rags, not to mention the complete absence of waterproofing and protection from precipitation;


— roofing felt - more durable than fiberglass, but excessively flammable, whole heating mains often burn out;
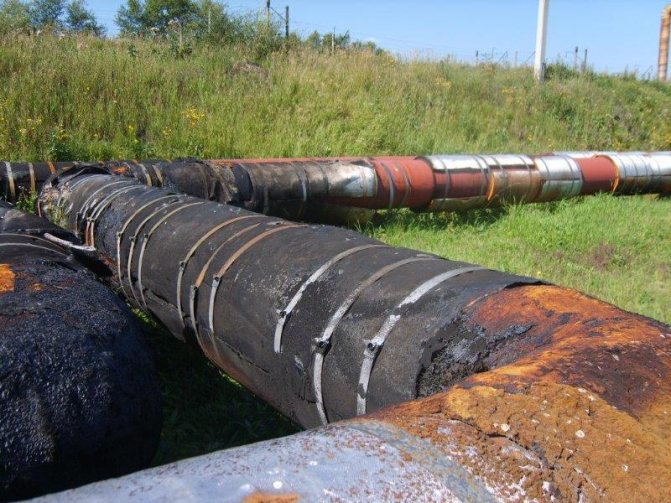


– galvanized - excellent material, durable and non-combustible, but its they steal very quickly... If the heat pipe passes outside the city limits or near suburban settlements, then, as a rule, galvanized sheets disappear the next morning after their installation.
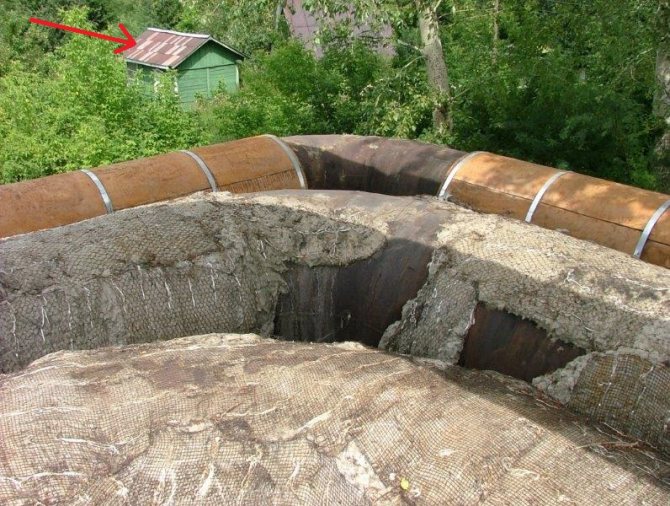


According to the recognition of the majority of heads of heat supply organizations, they have to restore heating mains hundreds of meters, which ultimately affects both the quality of the provided utilities and the costs associated with the operation of heating networks, which exceed all conceivable limits. However, there is a way out. Protection of the heat-insulating layer of external heating mains can be performed using heat-shrinkable tape TIAL-LCP. It is non-flammable, has an attractive appearance, does not lose its protective properties when exposed to low or high temperatures. In this case, the heating main will be as efficient and durable as possible.
| TIAL-LCP Thermal insulation tape layer of external heating mains >> |
Multilayer structures for pipeline protection
Often, pipe-in-pipe insulation is used to insulate pipelines. Using this diagram, a heat shield is installed. The main task of the specialists installing such a circuit is to correctly connect all the parts into a single structure.
Upon completion of the work, a structure is obtained that looks like this:
- a pipe made of metal or polymer material acts as the basis of the heat-shielding circuit. She is the supporting element of the entire device;
- heat-insulating layers of the structure are made of foamed polyurethane foam. The application of the material is carried out according to the pouring technology, a specially created formwork is filled with the molten mass;
- protective cover. Galvanized steel or polyethylene pipes are used for its manufacture. The former are used for laying networks in an open space. The latter are used in cases where pipeline systems are laid in the ground using channelless technology. In addition, often when creating this type of protective casing in a heater based on polyurethane foam copper conductors are laid, the main purpose of which is to remotely monitor the state of the pipeline, including the integrity of the thermal insulation layer;
- if the pipes are delivered to the installation site assembled, then the welding method is used to connect them. Specialists use special heat-shrink sleeves to assemble a heat-shielding circuit. Or overhead couplings can be used, made on the basis of mineral wool, which are covered with a layer of foil.
About the thickness of the pipeline and equipment insulation
It is imperative to rely on standards to determine the permissible thickness for each specific equipment. In them, manufacturers write about what density is retained in the heat flux. SNiPs contain algorithms for solving various formulas along with the formulas themselves.
Video
To identify the minimum thickness of pipelines, in one case or another, a limit is determined according to the permissible values of losses in certain areas.
Polyurethane insulation
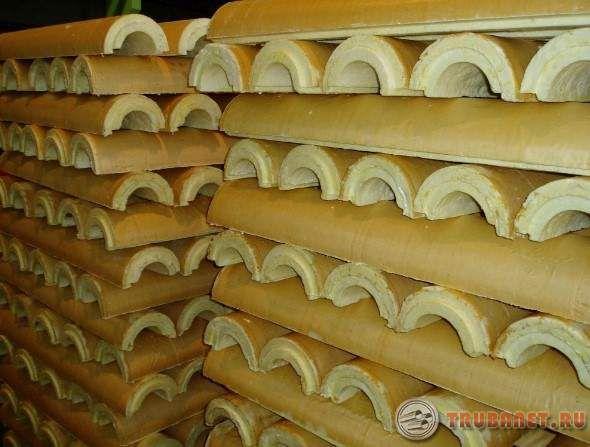


Pipelines with this type of insulation are used when it is necessary to lay a structure above the surface of the earth, channelless type. When manufacturing, they try to introduce as many new technologies as possible.
Of the materials, only those with the highest quality are allowed to the process. In advance, they are tested in large quantities, according to the joint venture, the thermal insulation of equipment and pipelines does not allow marriage.
The use of polyurethane foam allows to reduce heat losses. And provides durability for the insulation material itself. The polyurethane foam contains environmentally friendly components. These are Izolan-345, as well as Voratek CD-100. Compared to mineral wool, the thermal insulation performance of polyurethane foam is much higher.
PPM and APB insulation
For more than thirty years, the so-called polyfoam insulation has been used in pipelines. The main type in this case is polymer concrete. Its characteristics can be described as follows:
- Inclusion in the G1 group during flammability tests in accordance with the current GOST.
- Operating temperature, allowing you to maintain 150 degrees.
- The presence of an integral type structure, which combines the functions of a waterproofing coating together with a layer of insulation from heat.
Until recently, some regional manufacturers were engaged in the production of reinforced foam concrete insulation. This material has a very low density. On the other hand, thermal conductivity is a pleasant surprise.
Video
APB has the following set of advantages:
- Durability.
- Waterproof coating with high vapor permeability.
- The equipment does not corrode.
- The ability of the pipeline to withstand high temperatures.
- Fire resistance.
Such pipes are good because they can be used for a coolant of almost any temperature. This applies to both networks not only with water, but also with steam. The type of gasket does not matter.
It is even possible to combine with underground channelless and channel varieties. But products with PU foam insulation are still considered a more technological solution.
About the coefficient of thermal conductivity
The equipment, while it is in operation, it becomes possible to humidify - this is what most of all affects the calculated coefficient of thermal conductivity.
Video
Special rules exist for the adoption of a coefficient that implies an increase in the thermal conductivity of insulation coatings. At the same time, they are based on GOSTs and SNiPs, but other factors cannot be dispensed with:
- soil moisture according to SP.
- The variety to which the material for thermal insulation belongs.
The coefficient is equal to one, if we are talking about pipes with polyurethane foam insulation, in a sheath of high density polyethylene. It does not matter what is the level of moisture in the soil where the equipment is installed. The other will be the coefficient for equipment and pipes with APB insulation, which have an integral structure. And allowing the possibility that the insulating layer may dry out.
- 1.1 - the level of the coefficient for structures placed in soils with a large amount of water, according to the joint venture.
- 1.05 - for soils where the amount of water is not so large.
In practical calculations, special engineering techniques are used. They usually take into account resistance to external influences from the environment. Double-pipe laying involves taking into account the mutual thermal influence of each of the elements on the others.
Optimal thickness and additional recommendations
One of the determining factors in choosing a suitable thickness is the cost factor. And these indicators can be determined individually for each specific region.
Video
There are other parameters that matter. Like the design temperature of the coolant. It is also important at what level the temperature in the environment is.
Diy thermal insulation device for pipelines
There are a number of factors on which the technology of creating an insulating layer on pipelines may depend. One of the most important is how the collector is laid - from the outside or its installation is carried out in the ground.
Insulation of underground networks
To solve the problem of ensuring thermal protection of buried utilities, insulation work is carried out in the following order:
- first, sewer trays are laid at the bottom of the trench;
- after that, pipes are laid on top of them, after which they begin to seal the connections between them;
- then jackets are put on the pipes, and then the structure is wrapped with a vapor-proof fiberglass. Clamps made of polymer materials are used to fix the materials;
- then the tray is closed with a lid, after which it is covered with soil. Into the gap between him and the trench sand-clay laying is in progress mixtures followed by careful compaction;
- if there are no trays, then the pipes are laid on compacted soil with sand and gravel mixture.
Regulatory regulation
Thermal insulation of equipment and pipelines is based on SNiP 2.04.14-88. It contains information on materials and methods of their use, and outlines the requirements for protective circuits.
This document contains such recommendations.
- Regardless of the temperature of the medium, it is necessary to insulate any system.
- To create a thermal insulation layer, ready-made and prefabricated structures are equally used.
- The metal parts of the networks must be protected against corrosion.
- It is advisable to use a multi-layer contour design. It includes insulation, vapor barrier and a protective layer of dense polymer, non-woven fabric or metal. Sometimes a reinforcing loop is installed, which does not allow porous materials to wrinkle and prevents pipe deformation.
The document contains formulas by which the thickness of each layer of a multi-layer structure is calculated.
On a note! Most of the requirements for thermal insulation of pipelines apply to high-power trunk networks. However, when arranging domestic water supply and sewerage systems on your own, it is worth familiarizing yourself with the document and taking into account its recommendations when designing and installing.


According to SNiP, thermal insulation is mandatory